Chan Cc The State of the Art of Electric and Hybrid Vehicles Proc Ieee 2002 90 247ã¢â“275
Types of Electrical Cars
Different types of electric cars changed and are developed continuously giving users and potential users choices. Today the world is increasingly familiar with the terms BEV, HEV, PHEV and FCEV. How does an electric car work? How an electric vehicle works is depend on the type. This commodity will briefly talk over the types and working principles of electrical cars or vehicles marketed in the Globe and Indonesia today.
An electric car is a vehicle that is fully or partially propelled by electric motors, using energy stored in rechargeable batteries. The showtime practical electric cars were produced in the 1880s. Electric cars were popular in the late 19th century and early on 20th century. Innovation and advanced evolution in internal combustion engines (ICE) and mass production of cheaper gasoline vehicles has led to a decline in the apply of electric vehicles.
———————————————
The development of free energy storage technology, especially battery technology, makes electric cars become more popular once again at this time. And so how an electric car piece of work really?
How Does An Electric Automobile Work? – General
When pedal of the car is pressed, and then:
- Controller takes and regulates electric energy from batteries and inverters
- With the controller set, the inverter then sends a certain amount of electric energy to the motor (according to the depth of force per unit area on the pedal)
- Electric motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy (rotation)
- Rotation of the motor rotor rotates the transmission so the wheels plow then the machine moves.
Notation: The working principle to a higher place is for bombardment electric vehicle (BEV) type.
———————————————
Types of Electrical Cars
At that place are iv (four) types of electric cars, with the following outline:
- Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV)
- Hybrid
- Hybrid Electrical Vehicle (HEV)
- Plug-in Hybrid Electrical Vehicle (PHEV)
- Fuel Prison cell Electric Vehicle (FCEV)
In brief, the organization architecture of the iv types of electric cars to a higher place tin exist seen in the following figure:
Yous can read more than detailed caption below.
———————————————
Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV)
A Battery Electrical Vehicle (BEV), likewise called All-Electric Vehicle (AEV), runs entirely on a battery and electric bulldoze train. This types of electrical cars do non have an ICE. Electricity is stored in a large battery pack that is charged by plugging into the electricity grid. The battery pack, in plough, provides power to one or more electric motors to run the electrical machine.
Architecture and Main Components of
 Components of BEV
Components of BEV
- Electric motor
- Inverter
- Bombardment
- Command Module
- Drive train
Working Principles of BEV
- Ability is converted from the DC bombardment to AC for the electrical motor
- The accelerator pedal sends a point to the controller which adjusts the vehicle's speed past irresolute the frequency of the Ac power from the inverter to the motor
- The motor connects and turns the wheels through a cog
- When the brakes are pressed or the electric auto is decelerating, the motor becomes an alternator and produces power, which is sent back to the battery
Examples of BEV
Volkswagen eastward-Golf, Tesla Model 3, BMW i3, Chevy Bolt, Chevy Spark, Nissan Foliage, Ford Focus Electric, Hyundai Ioniq, Karma Revera, Kia Soul, Mitsubishi i-MiEV, Tesla X, Toyota Rav4.
———————————————
Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV)
This blazon of hybrid cars is often called equally standard hybrid or paralel hybrid. HEV has both an Water ice and an electric motor. In this types of electric cars, internal combustion engine gets energy from fuel (gasoline and others type of fuels), while the motor gets electricity from batteries. The gasoline engine and electric motor simultaneously rotate the transmission, which drives the wheels.
The difference between HEV compared to BEV and PHEV is where the batteries in HEV can only charged by the Ice, the movement of the wheels or a combination of both. There is no charging port, so that the battery cannot be recharged from outside of the organization, for example from the electricity grid.
Architecture and Primary Components of HEV
 Components of HEV
Components of HEV
- Engine
- Electric motor
- Battery pack with controller & inverter
- Fuel tank
- Command module
Working Principles of HEV
- Has a fuel tank that supplies gas to the engine like a regular car
- It as well has a set of batteries that run an electrical motor
- Both the engine and electric motor can plough the transmission at the aforementioned time
Examples of HEV
Honda Civic Hybrid, Toyota Prius Hybrid, Honda Civic Hybrid, Toyota Camry Hybrid.
———————————————
Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV)
PHEV is a type of hybrid vehicle that both an ICE and a motor, often chosen as series hybrid. This types of electrical cars offers a choice of fuels. This type of electric cars is powered by a conventional fuel (such as gasoline) or an alternative fuel (such bio-diesel) and by a rechargeable battery pack. The battery tin can exist charged upwards with electricity past plugging into an electrical outlet or electric vehicle charging station (EVCS).
PHEV typically tin can run in at least two modes:
- All-electrical Mode, in which the motor and bombardment provide all the car'due south free energy
- Hybrid Style, in which both electricity and gasoline are employed.
Some PHEVs tin travel more than seventy miles on electricity alone.
Architecture and Master Components of PHEV
 Components of PHEV
Components of PHEV
- Electric motor
- Engine
- Inverter
- Battery
- Fuel tank
- Control module
- Battery Charger (if onboard model)
Working Principles of PHEV
PHEVs typically showtime upward in all-electrical fashion and operate on electricity until their battery pack is depleted. Some models shift to hybrid way when they reach highway cruising speed, by and large above 60 or 70 miles per hr. Once the battery is empty, the engine takes over and the vehicle operates as a conventional, non-plug-in hybrid.
In addition to plugging into an outside electric power source, PHEV batteries can be charged by an internal combustion engine or regenerative braking. During braking, the electric motor acts as a generator, using the energy to charge the battery. The electric motor supplements the engine's ability; as a result, smaller engines tin can exist used, increasing the machine's fuel efficiency without compromising performance.
Examples of PHEV
Porsche Cayenne Southward E-Hybrid , Chevy Volt, Chrysler Pacifica, Ford C-Max Energi, Ford Fusion Energi, Mercedes C350e, Mercedes S550e, Mercedes GLE550e, Mini Cooper SE Countryman, Audi A3 E-Tron, BMW 330e, BMW i8, BMW X5 xdrive40e, Fiat 500e, Hyundai Sonata, Kia Optima, Porsche Panamera S E-hybrid, Volvo XC90 T8.
———————————————
Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle (FCEV)
Fuel Prison cell Electric Vehicles (FCEVs), also known every bit fuel cell vehicles (FCVs) or Zero Emission Vehicle, are types of electric cars that employ 'fuel prison cell technology' to generate the electricity required to run the vehicle. In this type of vehicles, the chemic energy of the fuel is converted directly into electric energy.
Compages and Main Components of FCEV
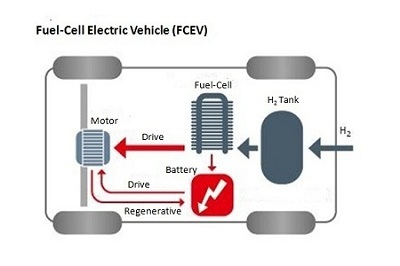 Components of FCEV
Components of FCEV
- Electric motor
- Fuel-cell stack
- Hydrogen storage tank
- Battery with converter and controller
Working Principles of FCEV
The working principle of a 'fuel prison cell' electric automobile is different compared to that of a 'plug-in' electrical car. This types of electric cars is because the FCEV generates the electricity required to run this vehicle on the vehicle itself.
Examples of FCEV
Toyota Mirai, Hyundai Tucson FCEV, Riversimple Rasa, Honda Clarity Fuel Jail cell, Hyundai Nexo.
———————————————
Contact Omazaki Group for consultancy and planning to install EVCS in Indonesia for domestic, commercial and industrial purposes, and public EVCS as well. For training related to electrical vehicles (EV), please download the complete list and catalog at Omazaki Grooming.
Related Articles:
- Electric Car Components and Functions
- Electric Car Batteries and Characteristics
- Electric Vehicle Charging Station (EVCS)
- Wireless Electric Vehicle Charging Stations (WEVCS) Engineering science
References:
- https://www.caa.ca/electric-vehicles/types-of-electric-vehicles/#bev
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electric_car
- https://world wide web.seai.ie/technologies/electric-vehicles/what-is-an-electric-vehicle/types-of-electric-vehicle/
- https://www.evgo.com/why-evs/types-of-electric-vehicles/
- http://world wide web.ieahev.org/about-the-technologies/plug-in-hybrid-electric-vehicles/
- Kenneth Barnett – The Hybrid Automobile: A look at the future of car
- https://www.conserve-energy-future.com/howelectriccarswork.php
- https://www.pkw-label.de/alternative-antriebe/elektrofahrzeuge-bevphevreev
- https://world wide web.elektromobilitaet.nrw/infos/eastward-machine/?L=0
Source: https://www.omazaki.co.id/en/types-of-electric-cars-and-working-principles/
0 Response to "Chan Cc The State of the Art of Electric and Hybrid Vehicles Proc Ieee 2002 90 247ã¢â“275"
Post a Comment